Value Based Care Models Explained
Value-based care models have become a cornerstone in the healthcare industry, focusing on delivering high-quality patient care while reducing costs and improving health outcomes. This approach marks a significant shift from traditional fee-for-service models, where healthcare providers are paid for each service rendered, to a system where payment is tied to the value of care provided. The core principle behind value-based care is to align incentives with quality and efficiency, thereby enhancing patient satisfaction and the overall effectiveness of healthcare services.
Introduction to Value-Based Care Models

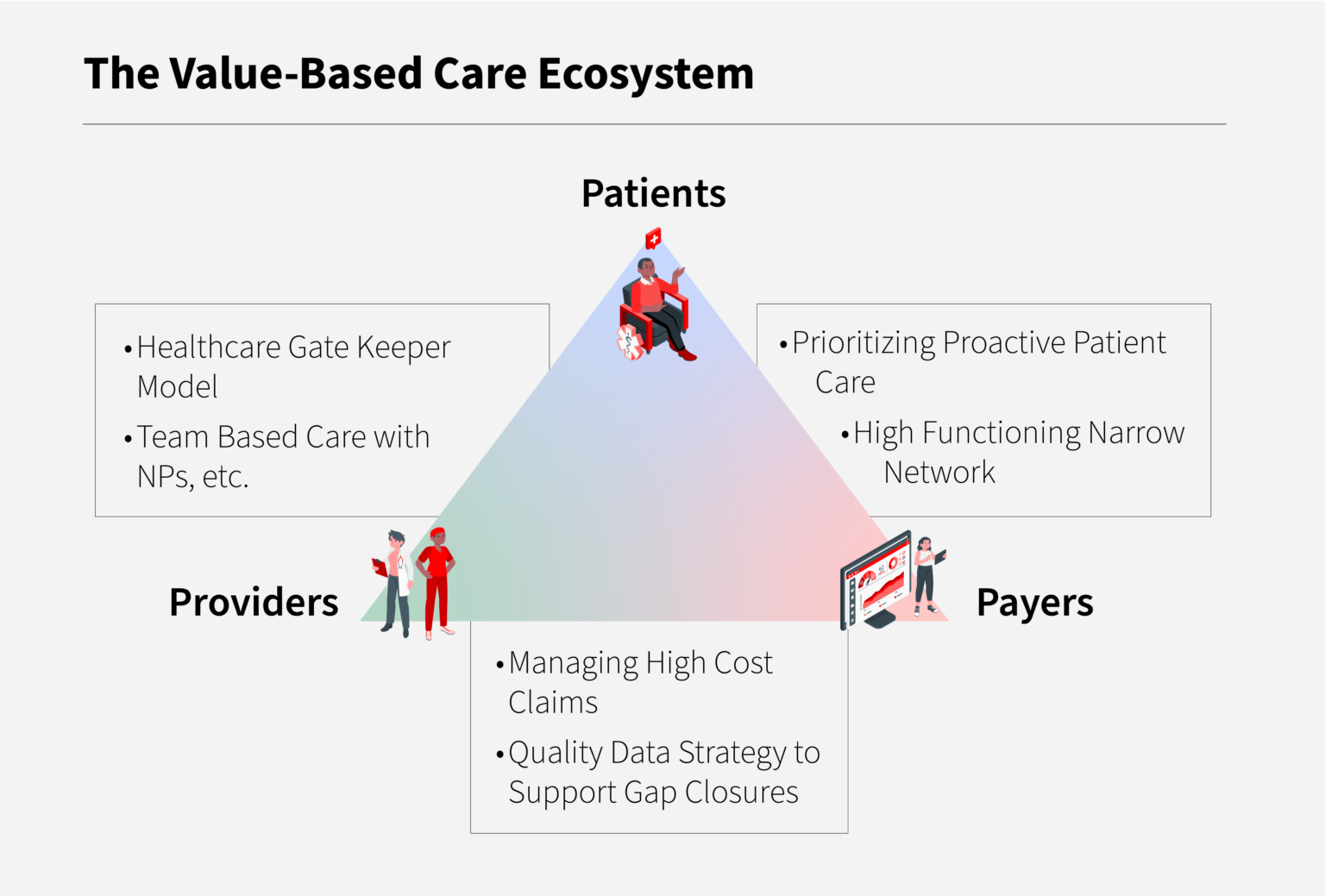
Value-based care models are designed to reward healthcare providers for delivering high-quality, patient-centered care that improves patient outcomes while controlling costs. These models incentivize providers to focus on preventive care, manage chronic conditions more effectively, and reduce unnecessary hospitalizations and readmissions. By doing so, value-based care aims to address some of the key challenges facing healthcare systems worldwide, including rising healthcare costs, inconsistent quality of care, and the need for more patient-centric approaches.
Key Components of Value-Based Care Models
Several key components are integral to the success of value-based care models. These include data analytics and reporting, which enable the measurement of quality and cost metrics; population health management, which involves proactive management of patient populations to prevent illness and manage chronic conditions; and care coordination, ensuring that patients receive seamless, comprehensive care across different healthcare settings. Additionally, value-based payment models play a crucial role, as they provide the financial incentives for healthcare providers to adopt value-based care practices.
| Value-Based Care Model | Description | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) | Networks of healthcare providers that work together to deliver coordinated care | Shared savings, quality metrics, care coordination |
| Bundled Payments | Single payment for all services related to a treatment or condition | Episode-based care, cost savings, quality improvement |
| Pay-for-Performance (P4P) | Payment based on meeting specific quality and efficiency metrics | Quality benchmarks, incentive payments, performance measurement |
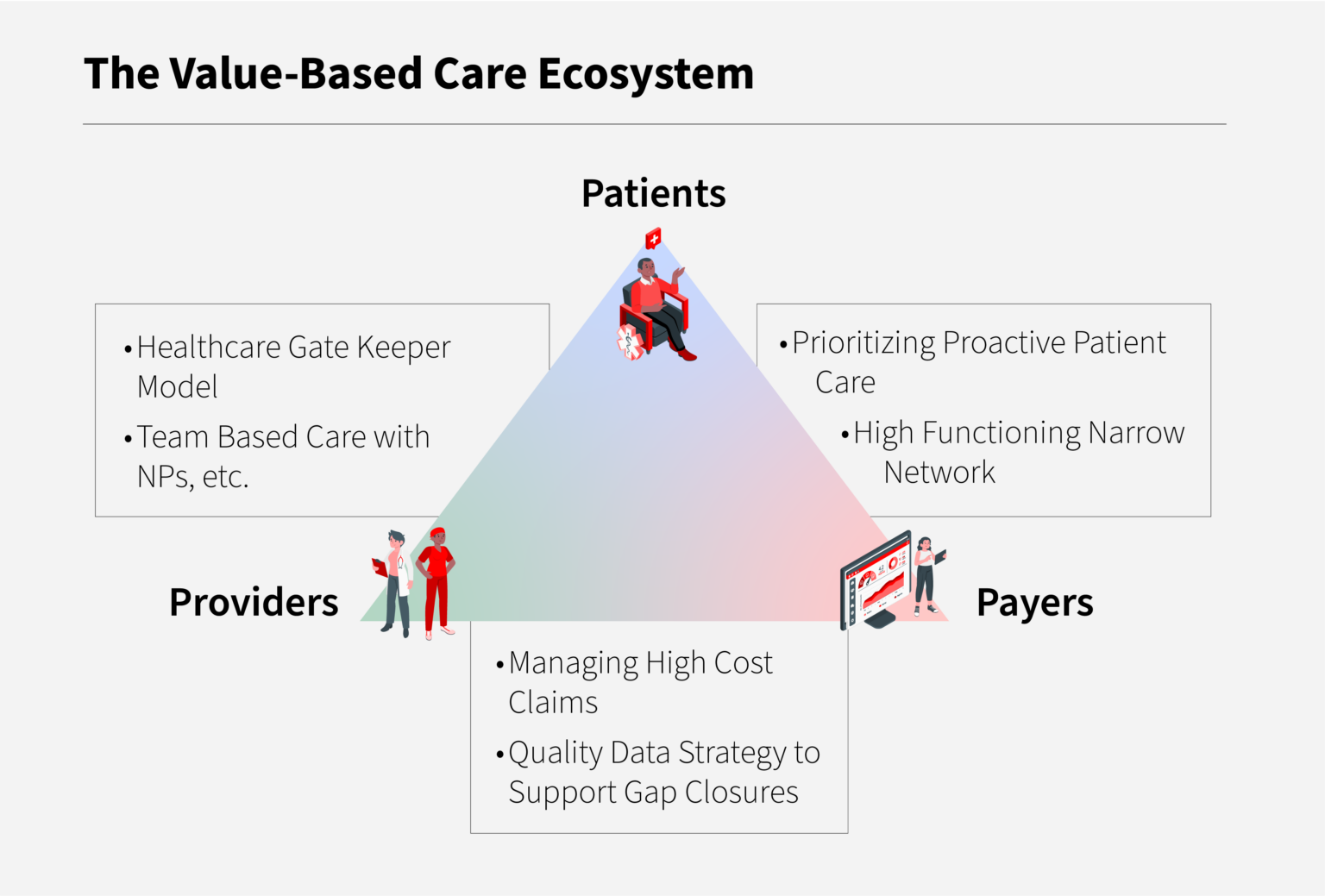
Benefits and Challenges of Value-Based Care Models
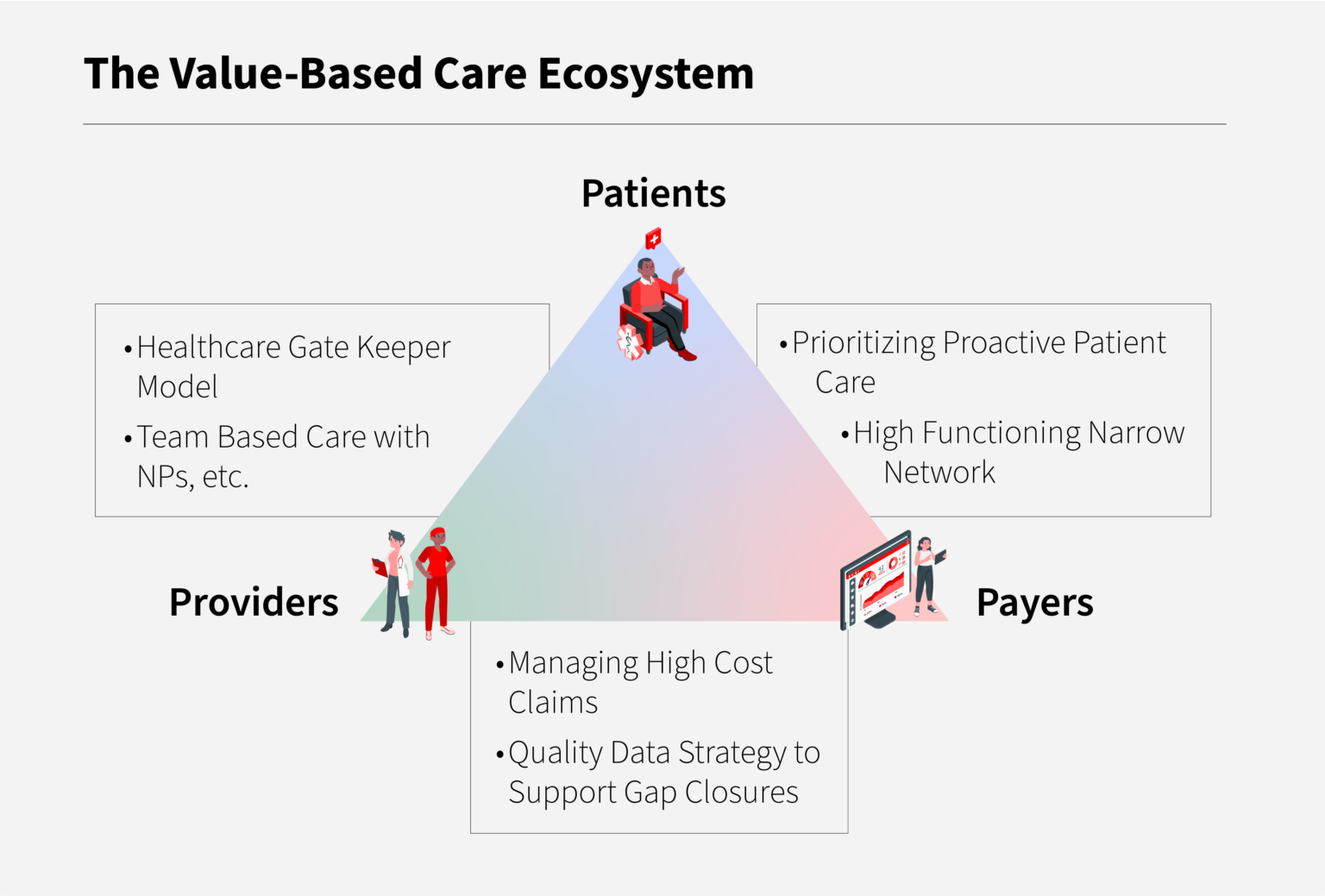
The adoption of value-based care models offers numerous benefits, including improved health outcomes, as care is more focused on prevention and management of chronic conditions; enhanced patient satisfaction, through more patient-centered care; and cost savings, achieved by reducing unnecessary services and improving efficiency. However, challenges also exist, such as the need for significant infrastructure investments in technology and data analytics, and the complexity of transitioning from traditional payment models, which can require substantial changes in healthcare delivery and financing structures.
Future of Value-Based Care
The future of healthcare is likely to be shaped significantly by value-based care models. As these models continue to evolve, we can expect to see greater emphasis on personalized medicine, where care is tailored to the individual needs and preferences of patients; telehealth and digital health technologies, which can expand access to care and improve patient engagement; and integrated care systems, where different healthcare services are coordinated to provide seamless care pathways. The success of value-based care will depend on the ability of healthcare systems to adapt to these changes and to continually improve the quality, accessibility, and affordability of care.
In conclusion, value-based care models represent a significant shift in the approach to healthcare delivery and financing. By focusing on quality, efficiency, and patient satisfaction, these models have the potential to address some of the major challenges facing healthcare systems today. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the role of value-based care models is expected to grow, leading to better health outcomes, improved patient experiences, and more sustainable healthcare systems.
What are the primary goals of value-based care models?
+The primary goals of value-based care models are to improve the quality of patient care, enhance patient satisfaction, and reduce healthcare costs. These models aim to achieve better health outcomes while making healthcare more affordable and sustainable.
How do value-based care models differ from traditional fee-for-service models?
+Value-based care models differ significantly from traditional fee-for-service models. In fee-for-service models, healthcare providers are paid for each service rendered, which can lead to overutilization and higher costs. In contrast, value-based care models pay providers based on the quality and value of care provided, incentivizing them to deliver efficient, high-quality care that improves patient outcomes.
What role does technology play in the implementation of value-based care models?
+Technology plays a critical role in the implementation of value-based care models. It enables the collection, analysis, and sharing of data, which are essential for measuring quality and cost metrics, coordinating care, and engaging patients. Technologies such as electronic health records, telehealth platforms, and data analytics tools are vital for the success of value-based care initiatives.



